Material Jetting 3d printing is a technology that uses inkjet print heads to deposit small droplets of photopolymer resin or other materials onto a build platform layer by layer to create a 3D object.
Material Jetting (Comprehensive Guide)
In this article, we will learn about:
Table of Contents
What is Material jetting?
Material jetting is an additive manufacturing process where droplets of material are selectively jetted and cured to create a three-dimensional object. It involves the precise deposition of build and support materials onto a build platform, which is then cured by either ultraviolet light or heat. This technique allows for the production of multi-color and multi-material parts with high accuracy and speed. Material jetting 3d printing is similar to the process of 2D inkjet printing, but instead of printing on paper, it prints in 3D In Material jetting 3d printing, the photopolymer resin is deposited in a liquid state and then cured or solidified using ultraviolet (UV) light.
This allows for the creation of highly detailed, complex shapes with very fine features and smooth surfaces.
Material-jetting 3d printing can produce parts with layer thicknesses as small as 16 microns, making it one of the most precise 3D printing technologies available.
Material-jetting 3d printing is commonly used for prototyping, small-batch manufacturing, and in the production of highly detailed parts for a variety of industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical.
Material Jetting Applications?
Material-jetting 3d printing can be utilized in a variety of industries and applications due to its high accuracy and ability to print with multiple materials. Here are some examples:
- Product development: Material-jetting 3d printing is commonly used for rapid prototyping and product development due to its ability to produce high-quality and detailed parts quickly.
- Jewelry: Material-jetting 3d printing can produce intricate and detailed jewelry designs with high accuracy, making it a popular choice for the jewelry industry.
- Medical: Material-jetting 3d printing can produce medical models and devices with high accuracy, allowing for precise customization and patient-specific solutions.
- Aerospace: Material-jetting 3d printing can produce lightweight and complex parts for aerospace applications, such as turbine blades and fuel nozzles.
- Art and architecture: Material-jetting 3d printing can be used to produce detailed models and sculptures for art and architecture projects.
- Electronics: Material-jetting 3d printing can be used to produce complex electronic components and circuit boards.
- Education: Material-jetting 3d printing can be used in education to produce models and prototypes for science, engineering, and design courses.
Overall, material-jetting 3d printing is best suited for applications that require high accuracy and detailed parts, such as product development, jewelry, medical, aerospace, art and architecture, electronics, and education.
Material jetting 3d printing Working principle?
Here is the working principle of material-jetting 3d printing:
- Designing the model: First, a 3D model is designed using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software.
- Preparing the material: The material is prepared by melting or dissolving it into a liquid form.
- Loading the material: The liquid material is loaded into a container or cartridge, which is then attached to the printer.
- Jetting the material: The printer’s print head moves back and forth over the build platform, depositing droplets of material onto the platform. The droplets are jetted through a tiny nozzle in the print head and are deposited in a specific pattern based on the 3D model.
- Solidification: Once the droplets are deposited, they are solidified using various methods such as UV light, heat, or cooling. This ensures that the material remains in place and forms a solid layer.
- Layer by layer: The process is repeated layer by layer until the entire 3D model is printed.
- Post-processing: Once the printing is complete, the object may need to undergo post-processing such as curing, polishing, or painting to achieve the desired finish.
Material Jetting Procedure:
Material-Jetting 3d printing is a technology that uses inkjet print heads to deposit small droplets of photopolymer resin or other materials onto a build platform layer by layer to create a 3D object.
steps involved in material jetting 3d printing working in detail:
Designing the 3D model: The first step in material jetting 3d printing is to create a 3D model of the object you want to print using 3D modeling software. The model is saved as a digital file, which the 3D printer can read.
Prepare the material: In material jetting 3d printing, photopolymer resin is used as the printing material. The resin is prepared by mixing photopolymer liquid with a curing agent. The resin is then poured into a cartridge, which is loaded into the printer.
Build platform preparation:The build platform is prepared with a layer of adhesive or a release agent to help the printed part adhere to the platform during printing.Printing process:The printing process begins with the printer depositing a thin layer of the photopolymer resin onto the build platform using the inkjet print heads. The inkjet print heads are similar to those used in 2D printing, but instead of printing on paper, they deposit droplets of resin onto the build platform.Curing process:After each layer of resin is deposited, it is cured using UV light. This solidifies the resin and bonds it to the previous layer. The UV light is typically delivered through a projector or an array of UV LEDs.Repeating the process:The printer repeats the process of depositing and curing layers of resin until the final 3D object is complete.Post-processing:
Once the printing is complete, the printed part is removed from the build platform and washed in a solvent to remove any excess resin. The part is then cured in a UV oven to ensure that it is fully cured and hardened.
Material jetting 3d printing is a highly precise technology that allows for the creation of complex, detailed parts with a high level of accuracy and surface finish. However, it can be a relatively slow process compared to other 3D printing methods, and the materials used can be costly.
ALSO READ : Know is 3d printing is a design revolution or intellectual property nightmare
Material Jetting Materials list with specifications?
Material-Jetting 3d printing is a technology that can use a variety of materials. However, the most common material used in material jetting 3d printing is photopolymer resin.
Here are some specifications of the photopolymer resins used in material jetting:
Photopolymer resin:
Photopolymer resin is a liquid polymer that solidifies when exposed to UV light.
It is commonly used in material jetting 3d printing because of its high resolution and ability to produce parts with smooth surfaces and fine details.
- The resins used in material jetting have a viscosity of around 30-100 cP,
- A density of around 1.1-1.3 g/cm3,
- A curing wavelength of around 365-405 nm.
Wax:
Wax can also be used as a material in material jetting 3d printing. Wax parts can be used as investment casting patterns or for lost wax casting.
Wax materials used in material jetting 3d printing have
- a melting point of around 50-80°C
- a density of around 0.9-1.1 g/cm3.
Ceramic:
Ceramic materials can also be used in material jetting 3d printing. Ceramic parts produced by material jetting 3d printing can be used for prototyping or as final products in the low-volume production run.
Ceramic materials used in material jetting 3d printing typically have
- the particle size of around 1-10 microns
- a density of around 2.5-4.5 g/cm3.
Metal:
Metal materials can also be used in material jetting. Metal parts produced by material jetting can be used for prototyping or as final products in the low-volume production run.
Metal materials used in material jetting typically have
- the particle size of around 5-20 microns
- a density of around 6-9 g/cm3.
It’s worth noting that the specific materials used in material jetting can vary depending on the printer and the manufacturer of the printing materials.
Material-Jetting 3d printing types with their strengths, weaknesses, requirements, and specifications?
There are several types of material-jetting 3d printing, each with its own unique process and advantages. Here are some of the most common types:
- Polyjet
- Multijet
- Drop on Demand (DOD)
- Nanoparticle jetting
- Binder jetting
PolyJet material jetting :
PolyJet is a material-jetting 3d printing technology developed by Stratasys.
It uses multiple print heads to deposit droplets of photopolymer resin onto a build platform, which are then cured by UV light.
PolyJet printers can create parts with high resolution, fine details, and smooth surfaces.
They can also print in multiple materials and colors simultaneously, making them ideal for creating prototypes and small production runs.
Strengths of polyjet:
- High resolution and fine details.
- Smooth surface finish.
- Ability to print in multiple materials and colors.
- Can create parts with high accuracy and precision.
Weaknesses of polyjet:
- Limited build volume.
- Expensive to operate.
- Photopolymer resins can be brittle.
Requirements of polyjet:
- Photopolymer resin.
- UV light source for curing.
- Specialized software for 3D modeling.
Specifications of polyjet:
- Resolution: up to 16 microns.
- Build volume: up to 490 x 390 x 200 mm.
- Material options: photopolymer resins
MultiJet material jetting:
MultiJet is a material-jetting 3d printing technology developed by 3D Systems.
It uses a print head to deposit droplets of photopolymer resin onto a build platform, which is then cured by UV light.
MultiJet printers can create parts with high resolution and fine details, but they typically have a lower build volume than PolyJet printers. They are also more limited in the types of materials they can print.
Strengths MultiJet :
- High resolution and fine details.
- Can print in multiple materials.
- Ideal for creating small, complex parts.
Weaknesses MultiJet:
- Limited build volume.
- Can be expensive to operate.
- Limited material options compared to PolyJet.
Requirements MultiJet:
- Photopolymer resin.
- UV light source for curing.
- Specialized software for 3D modeling.
Specifications MultiJet:
- Resolution: up to 32 microns.
- Build volume: up to 298 x 185 x 203 mm.
- Material options: photopolymer resins.
Drop-on-Demand material jetting 3d printing:
Drop-on-Demand (DOD) is a material jetting 3d printing technology that uses a single print head to deposit droplets of material onto a build platform.
The droplets are ejected from the print head on demand, rather than continuously.
DOD printers can create parts with high resolution and fine details, but they typically have a lower build volume than PolyJet and MultiJet printers.
They are also more limited in the types of materials they can print.
Strengths Drop-on-Demand:
- High resolution and fine details.
- Ability to print in multiple materials.
- Low cost compared to other material jetting technologies.
Weaknesses Drop-on-Demand:
- Limited build volume.
- Limited material options compared to PolyJet and MultiJet.
- The print head can get clogged.
Requirements Drop-on-Demand:
- Liquid material.
- Print head with piezoelectric actuator.
- Specialized software for 3D modeling.
Specifications Drop-on-Demand:
- Resolution: up to 10 microns.
- Build volume: up to 130 x 130 x 130 mm.
- Material options: liquids with low viscosity.
NanoParticle Jetting material jetting 3d printing:
NanoParticle Jetting is a material jetting 3d printing technology developed by XJet.
It uses a print head to deposit droplets of liquid material containing metal or ceramic nanoparticles onto a build platform.
The droplets are then heated to evaporate the liquid, leaving behind a solid part.
NanoParticle Jetting printers can create parts with high resolution and fine details in metal or ceramic materials.
Strengths NanoParticle Jetting :
- High resolution and fine details.
- Can print in metal and ceramic materials.
- Ideal for creating small, complex parts.
Weaknesses NanoParticle Jetting :
- Limited material options compared to PolyJet and MultiJet.
- Expensive to operate.
- Requires special handling for metal nanoparticle materials.
Requirements NanoParticle Jetting :
- Liquid material containing metal or ceramic nanoparticles.
- Print head with nozzle diameter of 100 microns or less.
- Specialized software for 3D modeling.
Specifications NanoParticle Jetting :
- Resolution: up to 10 microns.
- Build volume: up to 140 x 200 x 200 mm.
- Material options: metal or ceramic nanoparticles.
Binder Jetting material jetting 3d printing:
Binder Jetting is a material jetting 3d printing technology that uses a print head to deposit droplets of binder onto a bed of powder material, such as metal, sand, or ceramic.
The binder bonds the powder particles together, creating a solid part.
Binder Jetting printers can create parts with high resolution and fine details in a variety of materials, but they typically have a rougher surface finish than other material jetting technologies.
Strengths Binder Jetting:
- Ability to print in a variety of materials, including metals, sand, and ceramic.
- High build volume.
- Low cost compared to other material jetting technologies.
Weaknesses Binder Jetting:
- Rough surface finish compared to other material jetting technologies.
- Limited resolution and fine details.
Requirements Binder Jetting:
- Powder material.
- Binder material.
- Specialized software for 3D modeling.
Specifications Binder Jetting:
- Resolution: up to 100 microns.
- Build volume: up to 800 x 500 x 400 mm.
- Material options: metal, sand, ceramic.
In summary, each type of material jetting 3D printing has its own strengths and weaknesses, as well as specific requirements and specifications.
The choice of technology depends on the specific application and requirements of the project, such as desired resolution, material properties, and cost.
Material jetting advantages and Disadvantages over other 3d printing processes?
advantages and disadvantages when compared to other 3D printing processes, such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
Material Jetting advantages:
- High accuracy and resolution: Material-jetting 3d printing can produce very fine details and high-resolution parts due to its ability to jet very small droplets of material onto the build platform.
- Multi-material printing: Material-jetting 3d printing can print with multiple materials in a single build, allowing for the creation of complex geometries and the incorporation of multiple materials into a single part.
- Smooth surface finish: Material jetting 3d printing can produce parts with a smooth surface finish and high-quality surface detail.
- Wide range of materials: Material jetting 3d printing can print with a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites.
Material Jetting Disadvantages:
- High cost: material-jetting 3d printing can be an expensive process due to the cost of the printers, materials, and maintenance.
- Limited build size: material jetting 3d printing is limited in the size of parts it can produce due to the size of the build platform and the need for support structures.
- Post-processing requirements: material-jetting 3d printing may require post-processing, such as curing or polishing, to achieve the desired mechanical or surface properties.
- Slow printing speed: material-jetting 3d printing can be a slow process due to the need to deposit small droplets of material layer by layer.
In summary, material jetting 3d printing offers high accuracy, multi-material printing, smooth surface finish, and a wide range of materials, but has a high cost, limited build size, post-processing requirements, and slow printing speed.
Therefore, material jetting is ideal for applications that require high precision and intricate geometries but may not be suitable for large-scale or cost-sensitive projects.
Material Jetting 3d printer manufacturers:-
Stratasys’s Best Material Jetting 3d Printers
Stratasys is one of the largest 3D printing companies in the world and offers a range of material jetting 3D printing printers, including the J750 and Objet260 Connex.
Stratasys offers a variety of material jetting 3d printing printers, each with its own unique features and benefits. however, one of the best material jetting 3d printing printers is Stratasys J750
The Stratasys J750
The Stratasys J750 is a multi-material 3D printer that can print with up to six different materials at once, including rigid, flexible, transparent, and opaque materials, as well as materials with different colors and textures.
This allows for the creation of highly detailed and realistic prototypes and models.
The J750 also offers high resolution and precision, with layer thicknesses as low as 14 microns. It also includes an intuitive software interface that makes it easy to design and print complex models.
Overall, the Stratasys J750 is a versatile and powerful material-jetting 3D printer that is ideal for a wide range of applications, including product design, prototyping, and manufacturing.
Stratasys J750 Specification:
- Technology: Material Jetting (PolyJet)
- Layer Resolution: 14 microns (0.00055 in.)
- Build Size: 490 x 390 x 200 mm (19.3 x 15.35 x 7.9 in.)
- Material Capacity: Six cartridge bays, each containing 2.2 kg (4.85 lbs) of model material and support material
- Material Compatibility: Over 500,000 color combinations, including opaque, transparent, and flexible materials
- Connectivity: Ethernet, USB, WiFi
Stratasys J750 Price:
The Stratasys J750 is a high-end 3D printer and its price varies depending on the configuration, options, and location. However, the estimated price for the base model is around $300,000 USD.
Stratasys J750 Applications:
The Stratasys J750 is a multi-purpose 3D printer that is ideal for a wide range of applications, including:
- Prototyping and concept development
- Design validation and testing
- Medical modeling and simulations
- Art and jewelry design
- Education and research
Stratasys J750 Pros:
- Can print with up to six different materials at once, including rigid, flexible, transparent, and opaque materials
- Offers high-resolution and precision
- Can produce highly detailed and realistic prototypes and models with over 500,000 color combinations
- Easy-to-use software interface
- Suitable for a wide range of applications and industries
Stratasys J750 Cons:
- High initial investment cost
- Limited build volume compared to some other 3D printers
- Requires specialized training and maintenance
- Produces high levels of waste material during the support removal process
3D Systems Best Material Jetting 3d Printers
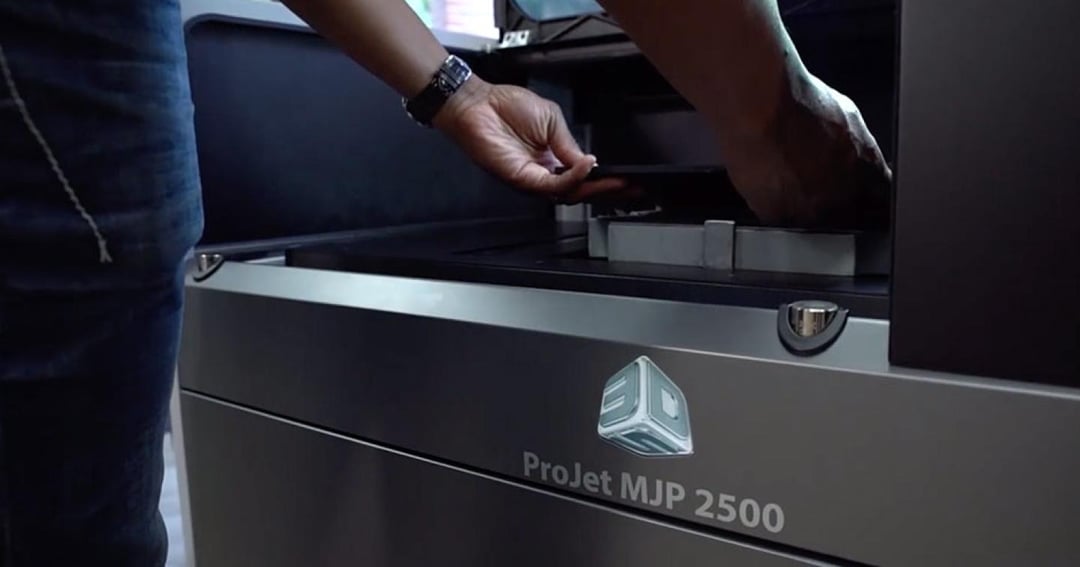
3D Systems offers a variety of Material Jetting 3D printers, including the ProJet MJP 2500 and ProJet 6000.
3D Systems offers a variety of material jetting 3D printers, each with its own unique features and benefits. However, one of their best Material Jetting 3D printers is the ProJet MJP 2500.
ProJet MJP 2500.
The ProJet MJP 2500 is a professional-grade 3D printer manufactured by 3D Systems.
It uses MultiJet Printing (MJP) technology, which involves jetting tiny droplets of material onto a build platform to create highly accurate and detailed parts.
With a build volume of 294 x 192 x 200 mm, the ProJet MJP 2500 is suitable for producing small to medium-sized parts with a resolution of up to 0.025 mm.
The printer can handle a variety of materials including VisiJet M3 materials, which offer a range of colors and material properties, making it ideal for applications in industries such as engineering, product design, and manufacturing. Additionally, the printer features an intuitive touchscreen interface and software that allows for easy print preparation and management
ProJet MJP 2500 Specification:
- Technology: Material Jetting (MultiJet Printing)
- Layer Resolution: 16 microns (0.0006 in.)
- Build Size: 294 x 192 x 200 mm (11.57 x 7.55 x 7.9 in.)
- Material Capacity: Four cartridge bays, each containing 1.5 kg (3.3 lbs) of model material and support material
- Material Compatibility: A range of materials, including rigid, flexible, and clear materials, as well as composite materials with high strength and temperature resistance
- Connectivity: Ethernet, USB, WiFi
ProJet MJP 2500 Price:
The price of the ProJet MJP 2500 varies depending on the configuration, options, and location. However, the estimated price for the base model is around $50,000 USD.
ProJet MJP 2500 Applications:
- The ProJet MJP 2500 is a versatile 3D printer that is ideal for a range of applications, including:
- Prototyping and concept development
- Design validation and testing
- Medical modeling and simulations
- Education and research
- Jewelry and art design
- Small batch production
ProJet MJP 2500 Pros:
- Offers high-resolution and precision
- Can produce parts with excellent surface finish and detail
- Supports a range of materials, including high-strength and temperature-resistant composites
- Easy-to-use software interface
- Suitable for a wide range of applications and industries
- Affordable compared to some other high-end material jetting 3D printers
ProJet MJP 2500 Cons:
- Limited build volume compared to some other 3D printers
- Requires specialized training and maintenance
- Produces high levels of waste material during the support removal process
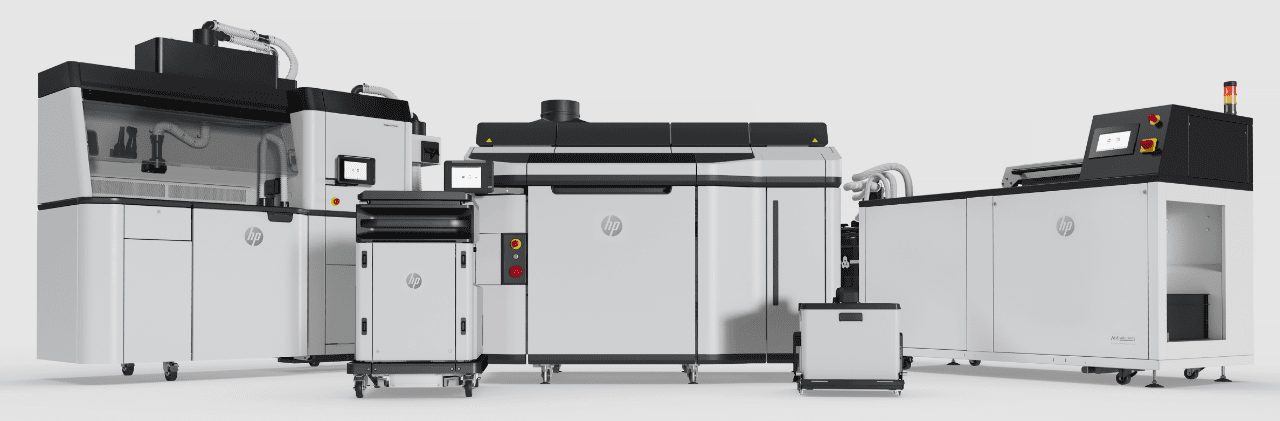
HP Best Material Jetting 3d Printing
HP’s Jet Fusion 3D printers use material jetting 3d printing technology to print high-quality parts quickly and efficiently.
HP offers a variety of 3D printers, including material jetting 3D printers. One of their best material jetting 3D printers is the HP Jet Fusion 5200 Series.
HP Jet Fusion 5200
The HP Jet Fusion 5200 is a powerful industrial 3D printing solution designed for high-volume manufacturing. It uses HP’s unique Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) technology, which involves fusing together layers of material using a combination of heat and pressure.
This allows for the production of parts with excellent mechanical properties, high precision, and consistent quality
HP Jet Fusion 5200 Specification:
- Technology: Material Jetting (Multi Jet Fusion)
- Layer Resolution: 1200 x 1200 dpi
- Build Size: 380 x 284 x 380 mm (15 x 11.2 x 15 in.)
- Material Capacity: Four cartridge bays, each containing 30 liters of model material and 40 liters of processing agents
- Material Compatibility: PA 11, PA 12, PA 12 Glass Beads, and PA 12GB Rigid materials
- Connectivity: Ethernet, USB
HP Jet Fusion 5200 Price:
The price of the HP Jet Fusion 5200 Series varies depending on the configuration, options, and location. However, the estimated price for the base model is around $250,000 USD.
HP Jet Fusion 5200 Applications:
The HP Jet Fusion 5200 Series is a versatile 3D printer that is ideal for a range of applications, including:
- Prototyping and concept development
- Design validation and testing
- Small batch production
- Manufacturing and end-use parts production
HP Jet Fusion 5200 Pros:
- Offers high-resolution and precision
- Can produce parts with excellent mechanical properties and isotropic strength
- Capable of printing functional parts with embedded sensors, electronics, and other components
- Supports a range of materials, including high-performance materials
- Suitable for a wide range of applications and industries
- Designed for industrial production environments
HP Jet Fusion 5200 Cons:
- High initial investment cost
- Limited material compatibility compared to some other 3D printers
- Requires specialized training and maintenance
- Produces high levels of waste material during the processing and recycling process
Mimaki Best Material Jetting 3d Printers
Mimaki’s 3DUJ-553 material jetting 3D printer uses UV-curable ink to create high-quality parts with vibrant colors.
EnvisionTEC Best Material Jetting 3d Printers
EnvisionTEC’s Micro Plus cDLM and Vida cDLM material jetting 3D printers use a patented Continuous Digital Light Manufacturing process to create high-resolution parts.
Optomec Best Material Jetting 3d Printers
Optomec’s Aerosol Jet 3D printers use a unique process that combines material jetting with aerosol deposition to create complex electronic components.
XJet Best Material Jetting 3d Printers
XJet’s Carmel 1400 and Carmel 700 material jetting 3D printers use a proprietary NanoParticle Jetting technology to print parts with high accuracy and detail.
Voxel jet Best Material Jetting 3d Printers
voxel jet’s VX2000 and VX4000 material jetting 3D printers are designed for industrial applications and can print large parts quickly and efficiently.
Rize Best Material Jetting 3d Printers
Rize’s XRIZE material jetting 3D printer uses patented Augmented Polymer Deposition technology to create high-strength parts with minimal post-processing.
Prodways Best Material Jetting 3d Printers
Prodways’ ProMaker P1000 and ProMaker P2000 material jetting 3D printers use proprietary MovingLight technology to print high-quality parts with excellent detail and accuracy.
FAQ
Multi-jet fusion technology VS Material Jetting 3d printing?
MULTI JET FUSION TECHNOLOGY VS MATERIAL JETTING 3D PRINTING DIFFERENCE
Technology | Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) | Material Jetting |
Materials | Powders | Liquid photopolymers |
Deposition | Fusing agent and detailing agent are jetted onto a bed of powdered material | Droplets of liquid photopolymer are jetted onto a build platform |
Build Volume | Up to 380 x 284 x 380 mm | Up to 490 x 390 x 200 mm |
Accuracy | High | Very high |
Surface Finish | Good | Very good |
Mechanical Properties | Excellent | Good |
Applications | Functional parts with mechanical properties | Detailed models and prototypes with high accuracy and resolution |











Glad you like it, definitely we will visit once